Expectant mothers are always looking for ways to provide their babies with the best nutrients. One of the most popular foods in pregnant women's diets is bird's nest, as it provides multiple benefits to both the mother and the child.
Before Pregnancy
According to research, eating bird's nests can have a positive effect on reproductive health. It has an excellent nutritional profile that helps to enhance reproduction and fertility by stabilising the reproductive cycle and increase embryo growth and survival. Besides, bird’s nest has been shown to have various health benefits, from strengthening the immune system to bone strength enhancement (read more here).
During Pregnancy & Postpartum
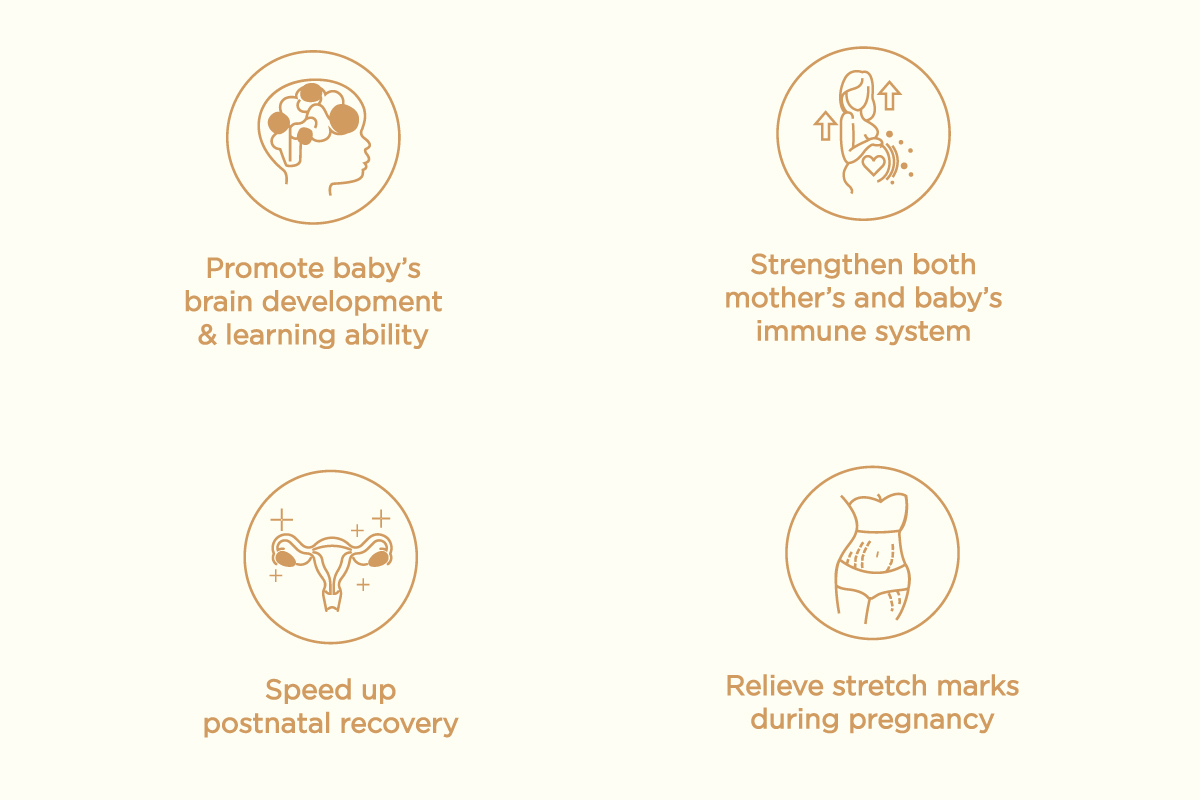
Promote baby’s brain development
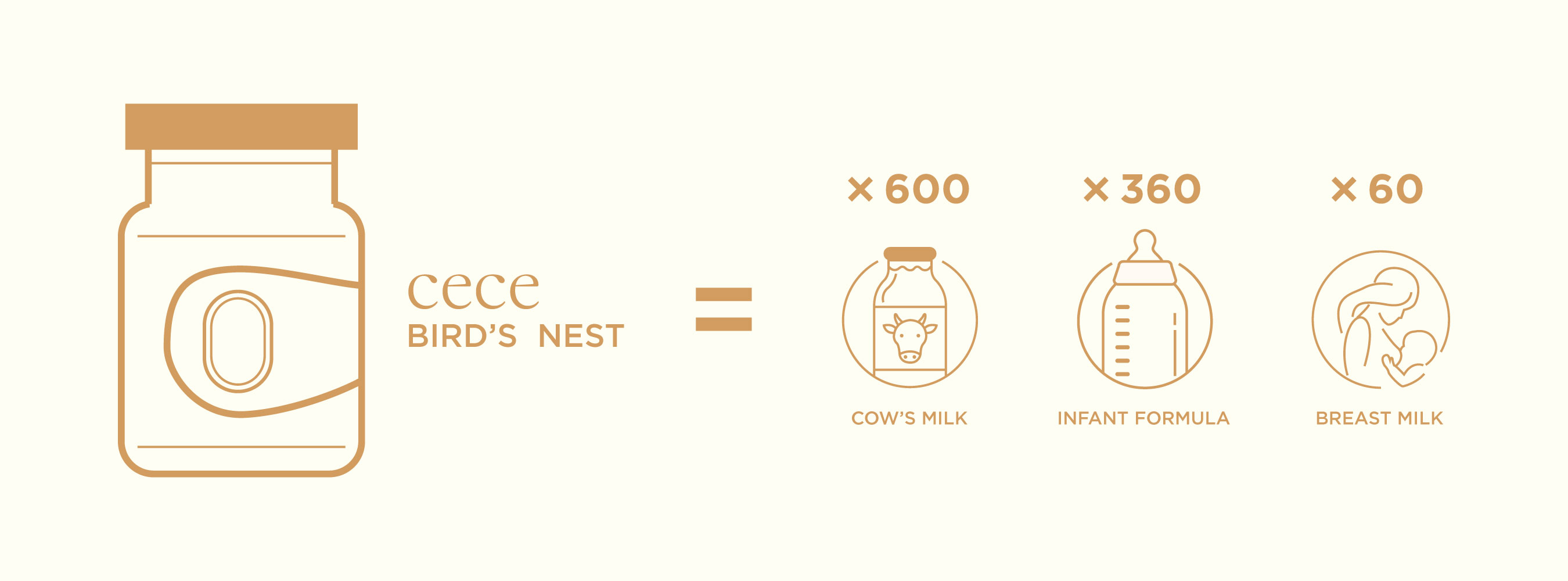
Breast milk is a newborn's best food, and the most important nutrition comes from sialic acid. It is a vital element that is responsible for healthy brain development and cognitive function in newborns. Studies have found that edible bird's nests contain 60x higher sialic acid content compared to breast milk. Pregnant and breastfeeding mothers who consume bird's nests have been proven to have a higher memory function and level of intelligence in their children.

Relieve postnatal stretch marks
For women who are expecting, the body undergoes enormous changes — and that includes stretch marks, which appear when rapid growth ruptures the collagen and elastin in your skin. The wonderful thing about bird’s nest is that it contains Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), which is very effective in treating postnatal stretch marks by regenerate tissue and promote collagen production.
How to consume?
For pregnant women, it is advised to consume after the first trimester.
To reap the health benefits of bird’s nest, it is advised to consume 3 grams of dried bird’s nest on a daily basis — anything additional will be excreted. The recommended way to consume bird's nest is by eating it on an empty stomach early in the morning or right before bed for best absorption.
Information written is strictly based on scientific papers. You may find the citations below for your reference.
Albishtue, A. A., Yimer, N., Zakaria, M. Z. A., Haron, A. W., Yusoff, R., Assi, M. A., & Almhanawi, B. H. (2018). Edible bird’s nest impact on rats’ uterine histomorphology, expressions of genes of growth factors and proliferating cell nuclear antigen, and oxidative stress level. Veterinary World, 11(1), 71–79. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2018.71-79
Carlson, S. E. (1985). N-Acetylneuraminic acid concentrations in human milk oligosaccharides and glycoproteins during lactation. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 41(4), 720–726. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/41.4.720
Marni, S., Marzura, M. R., Norzela, A. M., Khairunnisak, M., Bing, C. H., & Eddy, A. A. (2014). Preliminary Study On Free Sialic Acid Content Of Edible Bird Nest From Johor And Kelantan. Malaysian Journal Of Veterinary Research, 5(1), 9–14. http://www.dvs.gov.my/dvs/resources/user_15/mjvr%20v5.1/MJVR-V5N1-_p9-p14.pdf
Xie, Y., Zeng, H., Huang, Z., Xu, H., Fan, Q., Zhang, Y., & Zheng, B. (2018). Effect of Maternal Administration of Edible Bird’s Nest on the Learning and Memory Abilities of Suckling Offspring in Mice. Neural Plasticity, 2018, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7697261
Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Liu, L., Li, J., Du, G., & Chen, J. (2019). Microbial production of sialic acid and sialylated human milk oligosaccharides: Advances and perspectives. Biotechnology Advances, 37(5), 787–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.04.011
Join our newsletter to enjoy RM10 OFF on your first order
and be the first to hear about our exclusive updates!